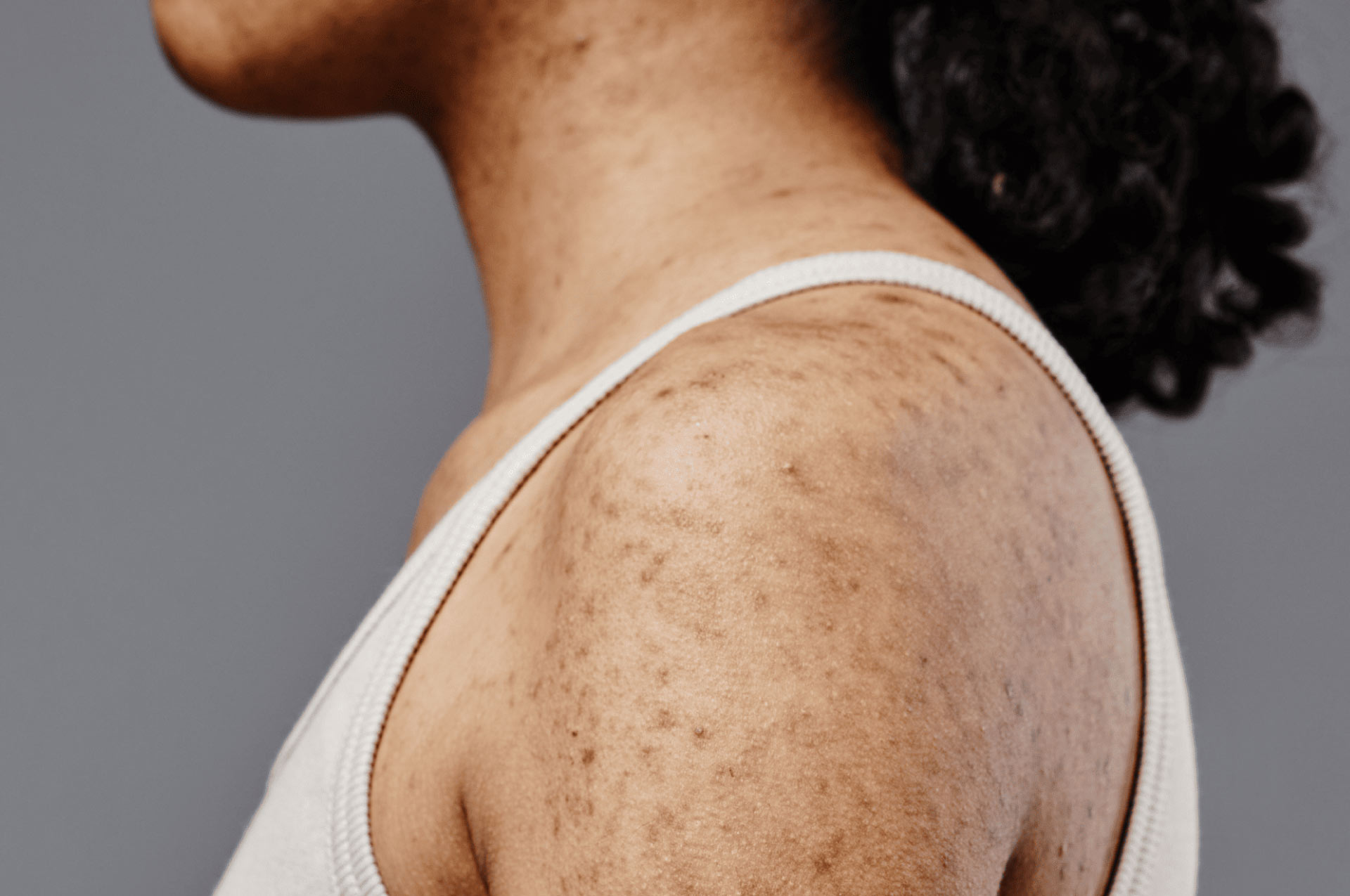
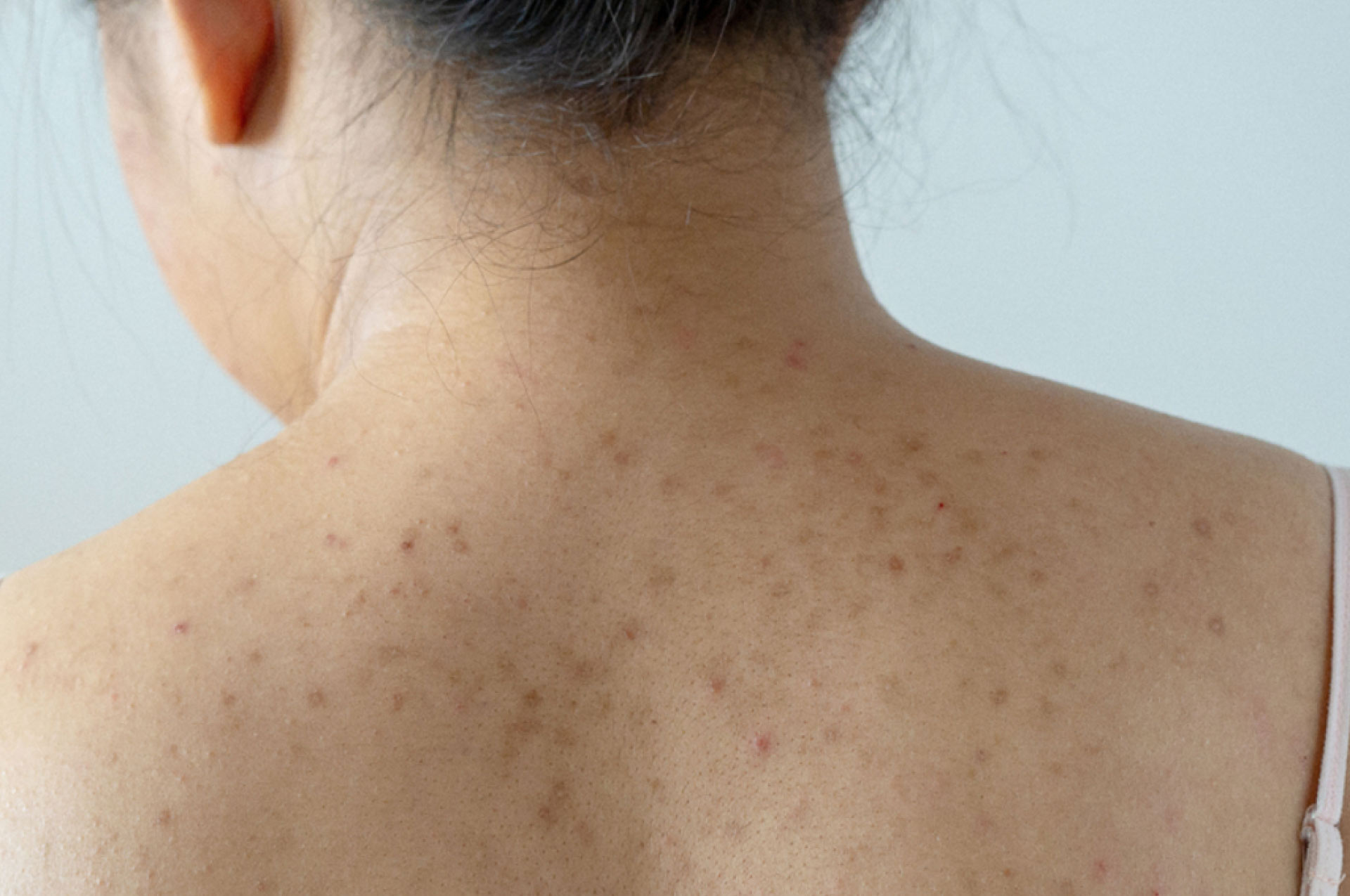
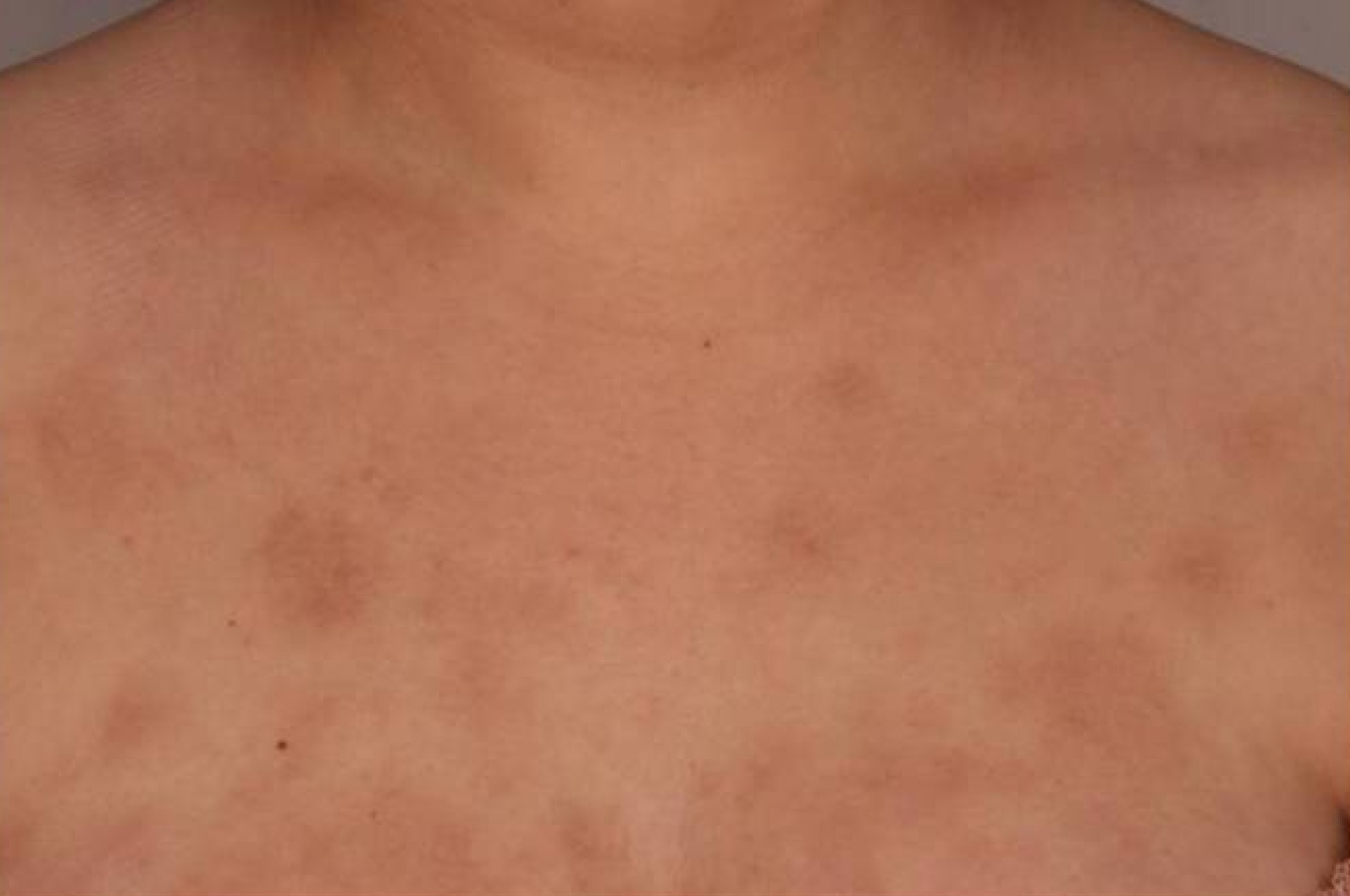
Sensitive skin is a condition when the skin overreacts to environmental factors, making it feel more sensitive than usual. People with sensitive skin experiencing this condition report exaggerated reactions when their skin is in contact with cosmetics, soaps and sun screens, and they often report worsening after exposure to dry and cold climate.
1- Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD):
Cause: Occurs when the skin is directly damaged by an irritating substance (e.g., soap, detergent, chemicals, friction). The reaction is due to the irritant’s direct effect on the skin.
Immune System Involvement: No immune response is involved; the reaction is localized and happens immediately or shortly after exposure.
Common symptoms: Redness, itching, pain, swelling, or blistering, depending on the severity of exposure.
2- Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD):
Cause: Occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that triggers an allergic response (e.g., poison ivy, nickel, certain fragrances). The skin has previously been sensitized to the substance, so the immune system reacts.
Immune system involvement: It involves an immune-mediated response (delayed hypersensitivity), where the body’s immune system recognizes and reacts to the allergen.
Common symptoms: Red, itchy rash, sometimes with blisters, that may take a day or more to appear after exposure.
3- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis):
Cause: Eczema is often linked to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema may have a genetic predisposition to dry, sensitive skin and a dysfunctional skin barrier, which makes the skin more susceptible to irritants and allergens. It’s not always triggered by direct contact with irritants or allergens, though these can worsen the condition.
Immune system involvement: Eczema involves an overactive immune response, leading to chronic inflammation in the skin.
Symptoms: Red, dry, itchy patches that can become thickened and cracked. It often flares up in response to triggers like stress, allergens, or weather changes.
People with sensitive skin experiencing this condition report exaggerated reactions when their skin is in contact with cosmetics, soaps and sun screens, a substance or material that causes sensitivity before, and they often report worsening after exposure to dry and cold climate.
Sensitive skin can present adverse reactions from itching, dryness, burning, erythema, stinging, or rash.
Self assessment is not always accurate to categorize skin as sensitive or not, especially if the skin reaction is caused by an allergic reaction, you have to take a series of skin tests and immunological tests to differentiate between the two.
1) Skincare patch test: before applying any new skincare product all over the face, apply small amounts of product in skin where it is easily sensitized such as the neck, your inner arm, and below your ears for at leasts 48 hours. If you have developed rash, redness, itchiness in these areas, you might have sensitive skin or sensitized to a certain substance.
2) if you are easily to develop redness, or itchiness, stinging, burning for new products then you are likely to develop sensitive skin.
3) If you have dry skin, you have more chances to develop sensitive skin.
Sensitive Skin (Long-term): A natural, often long-term skin condition where the skin is more prone to reactions from external factors like weather, skincare products, or allergens.
It is usually genetic and can be a result of having a weak skin barrier. People with conditions like rosacea, eczema, or naturally dry skin often have sensitive skin.
Sensitized Skin (Temporary): refers to skin that has become reactive or irritated due to external factors, but it’s not an inherent condition like sensitive skin.
Often caused by overuse of harsh products (e.g., exfoliants, strong acids), environmental damage (e.g., sun exposure, pollution), or aggressive treatments (e.g., laser or peels). It’s a temporary condition caused by external damage to the skin barrier.
Sensitized skin can be treated by focusing on strengthening and recovering the skin’s protective barrier. Use fragrance-free products, limit the use of actives, and simplify your skincare routine to include only the necessary steps: Cleanser, Moisturizer, and sunscreen.
1- Gentle cleansing. This means you should stay away from harsh surfactants like SLS/ sulfates. Look for ingredients like glycerin and avoid harsh soaps.
2- Moisturizing: Choose a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer. Ingredients like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and niacinamide can help soothe and repair the skin barrier. Make sure you don’t use a moisturizer with a high concentration of active ingredients in it, since high concentration of actives increase the skin’s sensitivity.
3- Serums: Always opt for a soft and gentle version of the active ingredients. For example if your skin needs to be exfoliated, opt for a gentle and hydrating acid at a low concentration like lactic acid. Do the same thing for retinoids, vitamin C, and other active ingredients.
4- Other beneficial tips:
-Do not use harsh scrubs or loofah on your skin. These large and sharp particles make small cuts on your face resulting in more sensitivity and possibly further damage.
-Do not use any DIY or homemade products on your skin, these products are usually poorly made and have not been put to the test by professionals and chemists. They can be easily infected with bacteria and germs due to the absence of adequate sanitary practices and the addition of preservatives and stabilizers.
-Do not use any suspicious products on your skin. Suspicious products that do not have the FULL ingredient list written on them, ambiguous language about the product and manufacturer (the product states the ingredient in a general way like:packed with vitamins and minerals but it does not specify which ones).
-Do not buy products that are not properly packaged, like when the outer box is damaged, has no protective plastic film, or when the seal on the bottle has been broken/opened.
-Make sure you watch out for copied, expired or not properly stored products, these can usually be sold at a cheaper price than the usual product in other credible stores and pharmacies.
-Always check the product’s reviews whether it is online, asking friends and family members or by checking the brand’s or manufacturer’s websites.